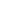
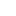Basic Structure
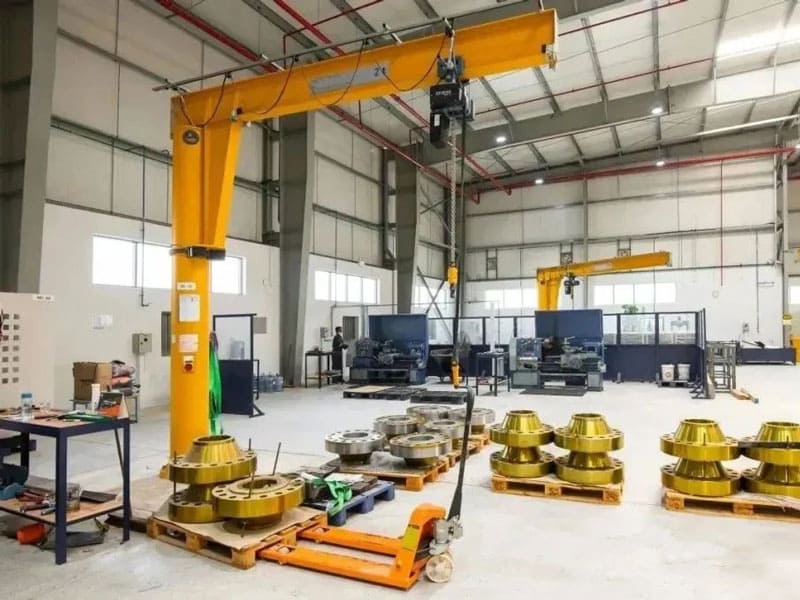
A pillar jib crane, also known as a column-mounted jib crane, is a versatile lifting device used in various industrial settings for material handling tasks. Its primary components include:
1.Pillar (Column): The vertical support structure that anchors the crane to the floor. It is usually made of steel and designed to bear the entire load of the crane and the lifted materials.
2.Jib Arm: The horizontal beam that extends from the pillar. It can rotate around the pillar, providing a wide working area. The arm typically features a trolley or hoist that moves along its length to position the load precisely.
3.Trolley/Hoist: Mounted on the jib arm, the trolley moves horizontally along the arm, while the hoist, attached to the trolley, raises and lowers the load. The hoist can be either electric or manual, depending on the application.
4.Rotation Mechanism: Allows the jib arm to rotate around the pillar. This can be manual or motorized, with the degree of rotation varying from a few degrees to a full 360°, depending on the design.
5.Base: The foundation of the crane, which ensures stability. It is securely anchored to the ground, often using a concrete foundation.


Working Principle
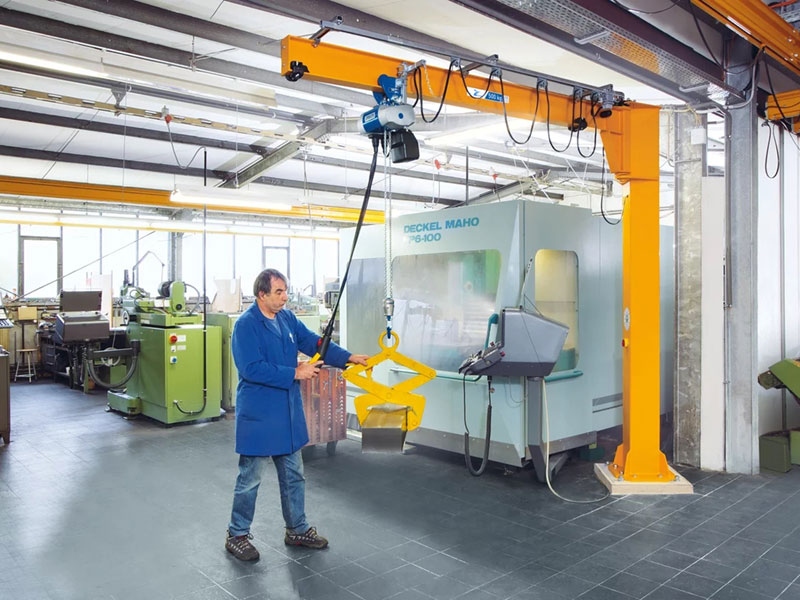
The operation of a pillar jib crane involves several coordinated movements to lift, transport, and position materials efficiently. The process can be broken down into the following steps:
1.Lifting: The hoist raises the load. The operator controls the hoist, which can be done via a control pendant, remote control, or manual operation. The hoist's lifting mechanism usually consists of a motor, gearbox, drum, and wire rope or chain.
2.Horizontal Movement: The trolley, which carries the hoist, moves along the jib arm. This movement allows the load to be positioned anywhere along the length of the arm. The trolley is typically driven by a motor or manually pushed.
3.Rotation: The jib arm rotates around the pillar, enabling the crane to cover a circular area. The rotation can be manual or powered by an electric motor. The degree of rotation depends on the crane's design and installation environment.
4.Lowering: Once the load is in the desired position, the hoist lowers it to the ground or onto a surface. The operator carefully controls the descent to ensure precise placement and safety.
Pillar jib cranes are highly valued for their flexibility, ease of use, and efficiency in handling materials in confined spaces. They are commonly used in workshops, warehouses, and production lines where space and mobility are critical.
Post time: Jul-12-2024